What is a communication system?
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
What is a communication system?
A telephone infrastructure or communication system consists of a set of independent telecommunications networks, transmitting facilities, relay stations, tributary stations and terminal equipment which are typically capable of being interconnected and interoperable in order to form an integrated system. The elements of the communication system serve a common function, are functionally consistent, use common methods, respond to controls and work in a union.
Telecommunications is a medium of contact (e.g. for sports television, mass media, journalism, etc.). Communication is the process of conveying the desired meanings from one person or party to another through the use of mutually recognised signs and semiotic laws.
Methods of Communication
- Face to face
- Signals
- Written word (letters)
- Electrical innovations:
- Telegraph
- Telephone
- Radio
- Television
- Internet (computer)
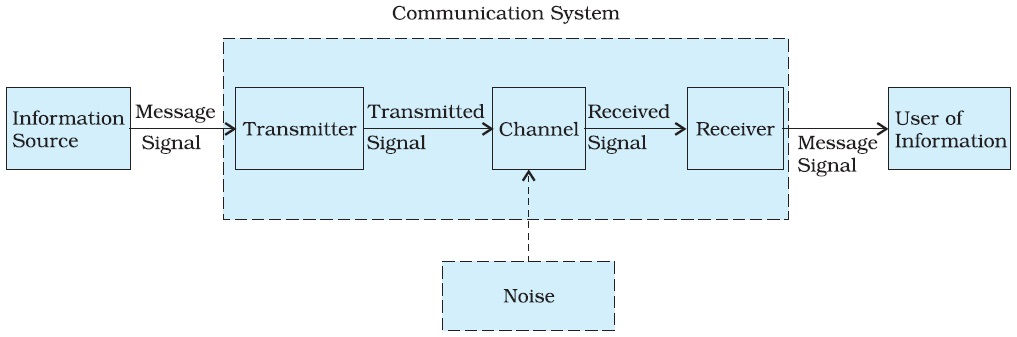
Basic Components of Communication System
- Transmitter
- Channel or medium
- Receiver
Transmitter
A transmitter is a collection of electronic components and circuits that converts the electrical signal into a signal suitable for transmission over a given medium. Transmitters are made up of oscillators, amplifiers, tuned circuits, filters, modulators, frequency mixers and frequency synthesizers.
Communication Channel
The communication channel is the medium by which the electronic signal is sent from one place to another. Types of media include electrical conductors, optical media, free space or system-specific media (e.g., water is the medium for sonar).
Receivers
A receiver is a collection of electronic components and circuits that accepts the transmitted message from the channel and converts it back into a form understandable by humans. Receivers contain amplifiers, oscillators, mixers, tuned circuits and filters and a demodulator or detector that recovers the original intelligence signal from the modulated carrier.
Transceivers
A transceiver is an electronic unit that incorporates circuits which send and receive signals. Examples include telephones, fax machines, handheld CB radios, cell phones and computer modems.
Attenuation
Signal attenuation or degradation, exists in all media of wireless transmission. It is proportional to the square of the distance between the transmitter and receiver.
Noise
Noise is random, undesirable electronic energy that enters the communication system via the communicating medium and interferes with the transmitted message.