Three Phae AC Power
Three-phase electrical control is a typical type of alternating electrical power production, transmission and distribution. This is a form of a polyphase network which is the most widespread method of transmission of power utilized by electrical grids worldwide. It is also used to power large engines and other heavy loads.
A three-wire three-phase circuit is usually more economical than an equivalent two-wire single-phase circuit on the same line to ground voltage because it uses less conductive material to transmit a given amount of electrical power.
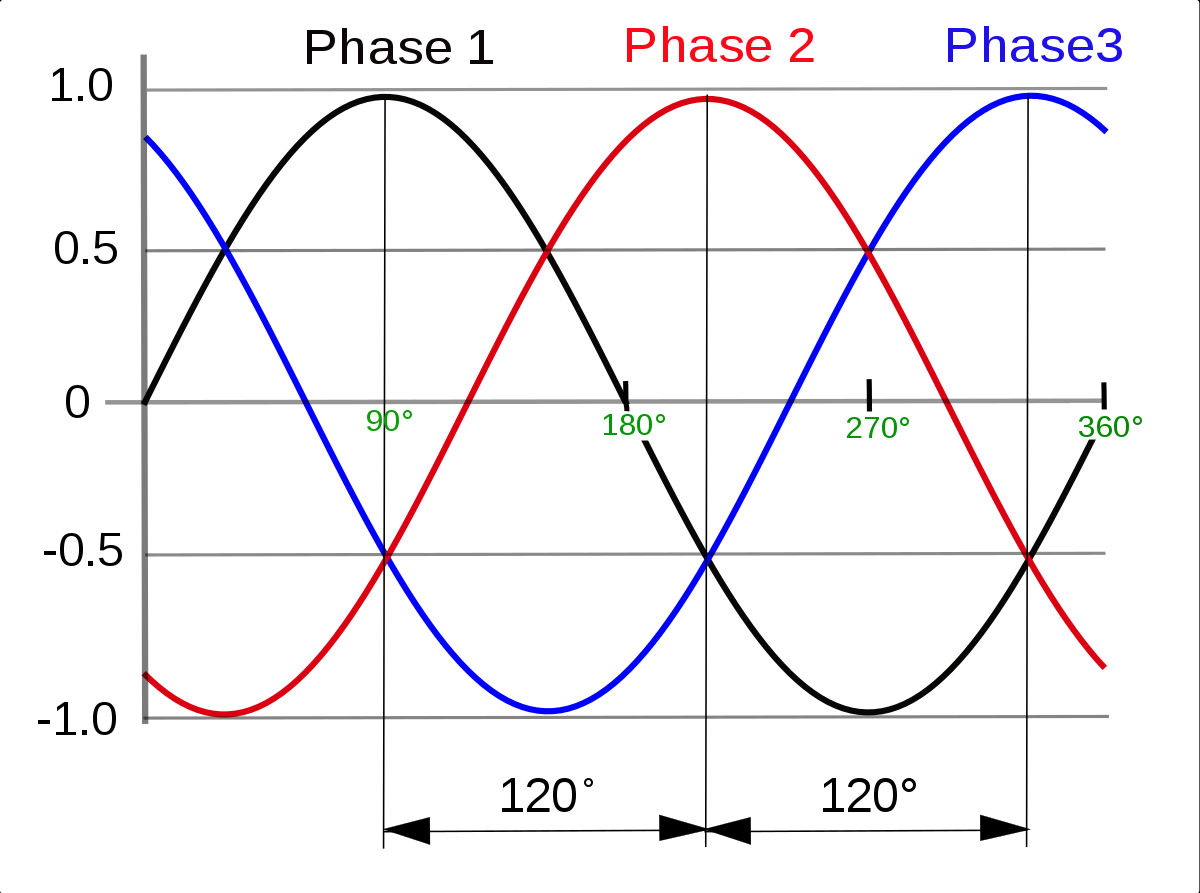
In an asymmetric three-phase power supply network, three conductors each bear an alternating current with the same frequency and voltage intensity compared to a standard reference but with a phase gap of one-third of each loop. The common reference is usually connected to the ground and often to a current conductor called a neutral conductor. Due to the difference in phase, the voltage on any conductor reaches its peak at one-third of the cycle after one of the other conductors and one-third of the cycle before the remaining conductor. This phase delay gives a constant transfer of power to a balanced linear load. It also allows the development of a spinning magnetic field in an electric motor and the creation of additional phase configurations utilizing transformers (for example, a two-phase device using a Scott-T transformer). The magnitude of the voltage differential between the two phases is Root(3) * (1.732 ...) times the magnitude of the voltage in each step.
The symmetrical three-phase systems mentioned here are commonly referred to as three-phase systems since, while asymmetric three-phase power systems (i.e. with irregular voltages or phase shifts) may be engineered and introduced, they are rarely used in operation since they lack the most significant advantages of symmetrical systems.
In a three-phase system feeding a balanced and linear load, the sum of the instantaneous currents of the three conductors is zero. In other words, the current in each conductor is equal in magnitude to the sum of the currents in the other two but with the opposite sign. The return path for the current in any phase conductor is the other two-phase conductors.
Advantages of Three-Phase Systems
Three-phase supplies have properties that make them very desirable in electric power distribution systems:
- The phase currents appear to cancel each other out, summing to zero in the case of a linear balanced load. This causes the scale of a neutral conductor to be minimized as it holds little to no current. For a balanced load, both phase conductors have the same current and should be of the same duration.
- The flow of power to a linear controlled load is continuous, which tends to reduce engine and motor noise.
- Three-phase systems can produce a rotating magnetic field with a specified direction and a constant magnitude, which simplifies the design of electric motors because no starting circuit is needed. Most household loads are single-phase.
In North American residences, three-phase power could be used to supply a multi-unit apartment block, but household loads are connected only as a single phase. Only a single process can be required for delivery in low-density regions. Any high-power household devices, such as electric stoves and clothes dryers, are operated by a 240-volt split-phase battery or by a 208-volt three-phase system.
Difference Between Single Phase & Three Phase
The power supply system is mainly classified into two types i.e., single-phase and the three-phase system. The single-phase is used in a place where less power is required and for running the small loads. The three phases are used in large industries, factories and in the manufacturing unit where a large amount of power is required. The differences between single and three phases are shown in the figure below.
How to identify a single phase and 3 phase?
The single-phase supplies the voltage up to 230V whereas the three-phase supply carries the voltage up to 415V.
Key Differences Between Single Phase and Three Phase
- In single-phase supply, the power flows through one conductor whereas the three-phase supply consists of three conductors for power supply.
- The single-phase supply requires two wires (one phase and one neutral) for completing the circuit. The three-phase requires three-phase wires and one neutral wire for completing the circuit.
- The single-phase supplies the voltage up to 230V whereas the three-phase supply carries the voltage up to 415V.
- The maximum power is transferred through three phases as compared to a single-phase supply.
- The single-phase has two wires which makes the network simple whereas the three-phase network is complicated as it consists of four wires.
- The single-phase system has only one phase wire, and if the fault occurs on the network, then the power supply completely fails. But in a three-phase system, the network has three phases, and if the fault occurs on any one of the phases, the other two will continuously supply the power.
- The efficiency of the single-phase supply is less as compared to the three-phase supply. Because the three-phase supply requires less conductor as compared to a single-phase supply for the equivalent circuit.
- The single-phase supply requires more maintenance and becomes costly as compared to the three-phase supply.
- The single-phase supply is mostly used in the house and for running the small loads. The three-phase supply is used in large industries and for running the heavy loads.